Fluid flow in fractured porous media
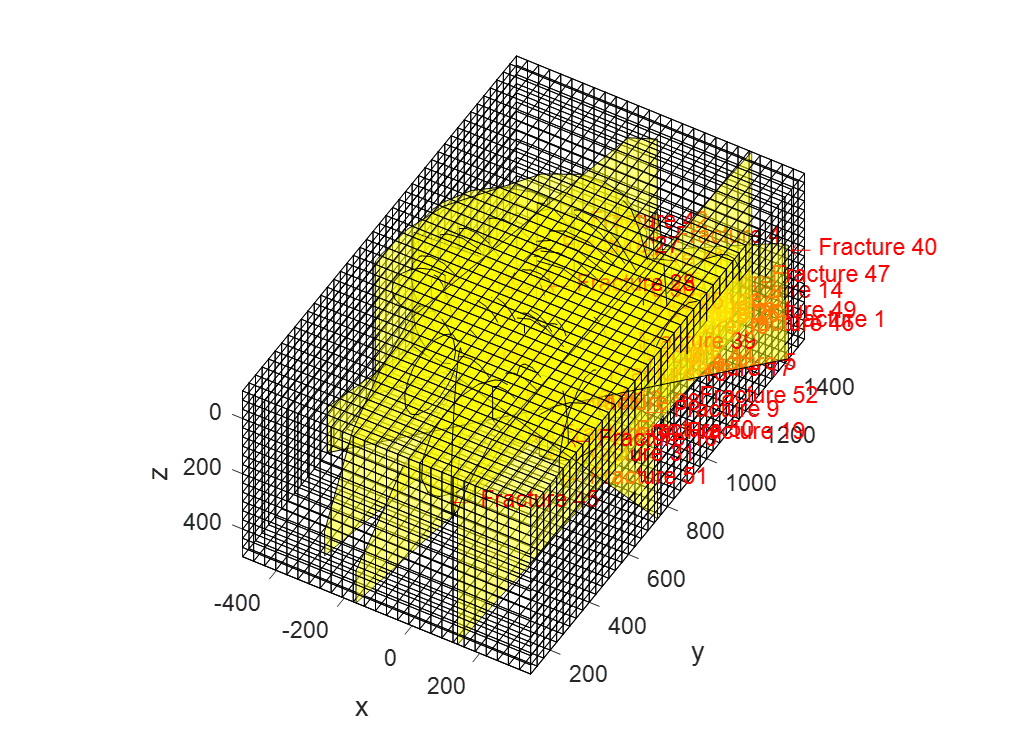
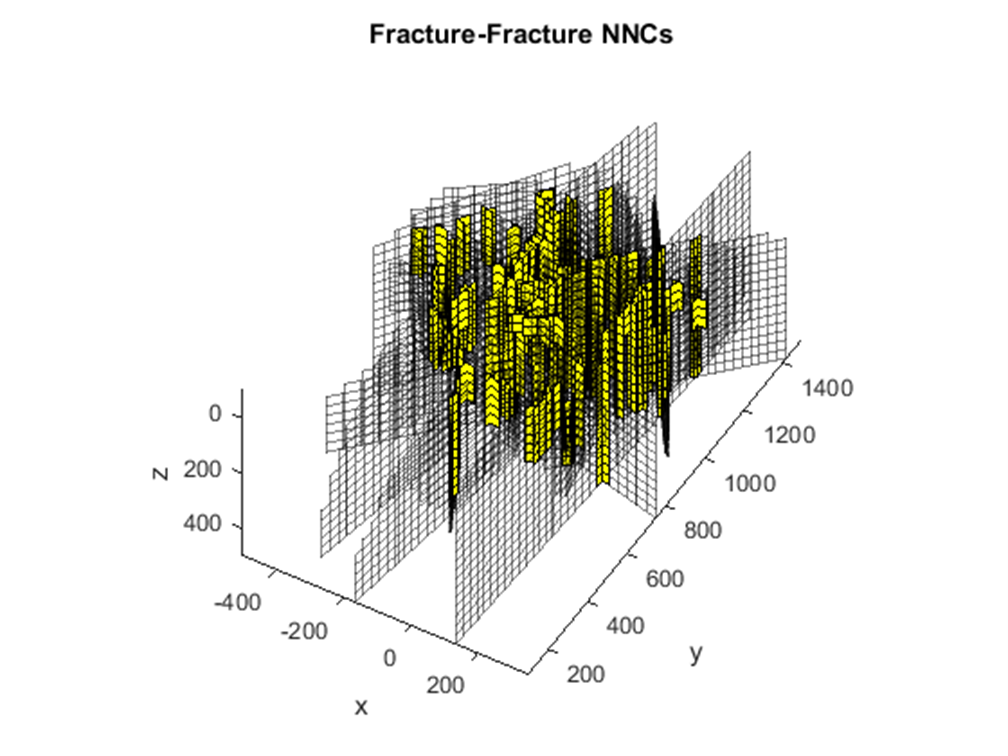
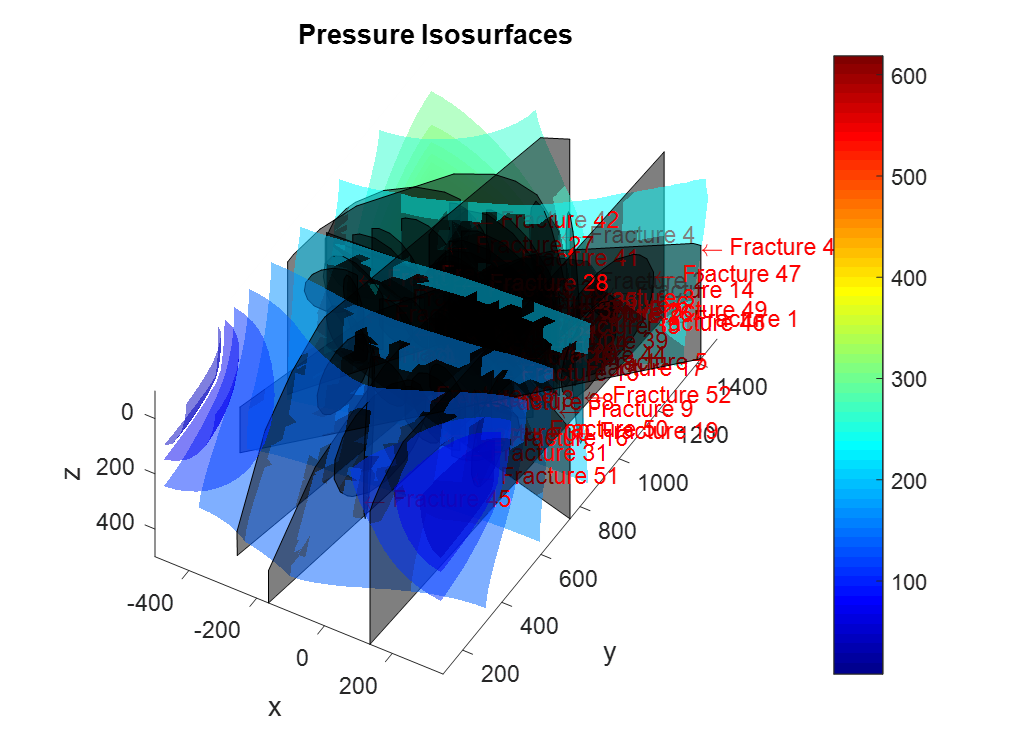
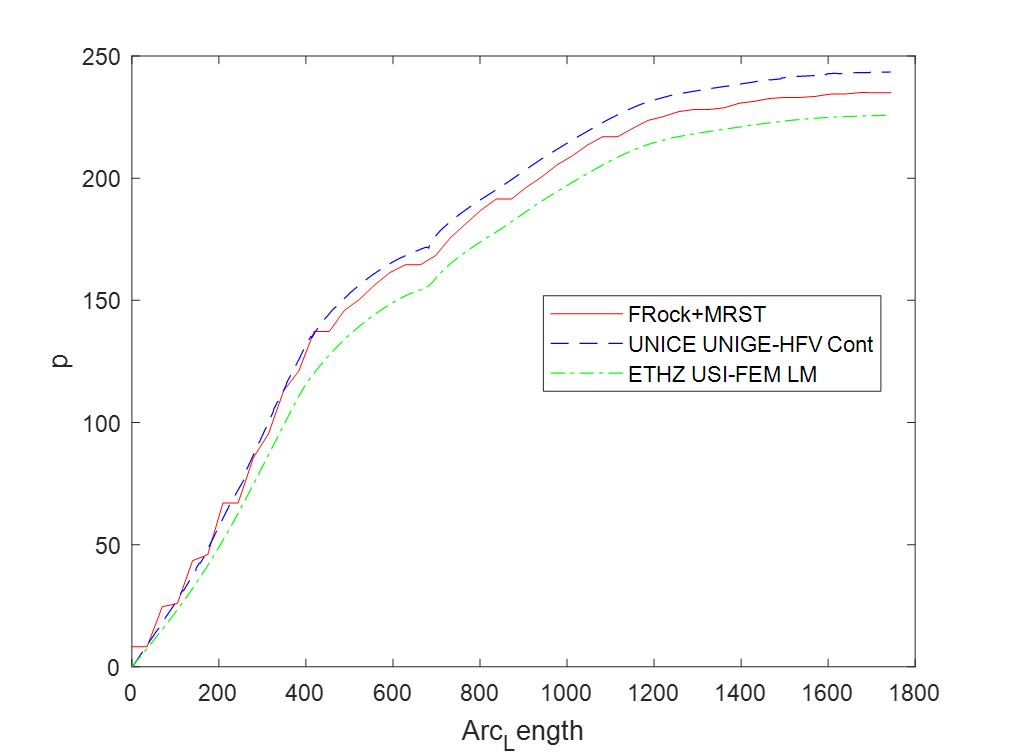
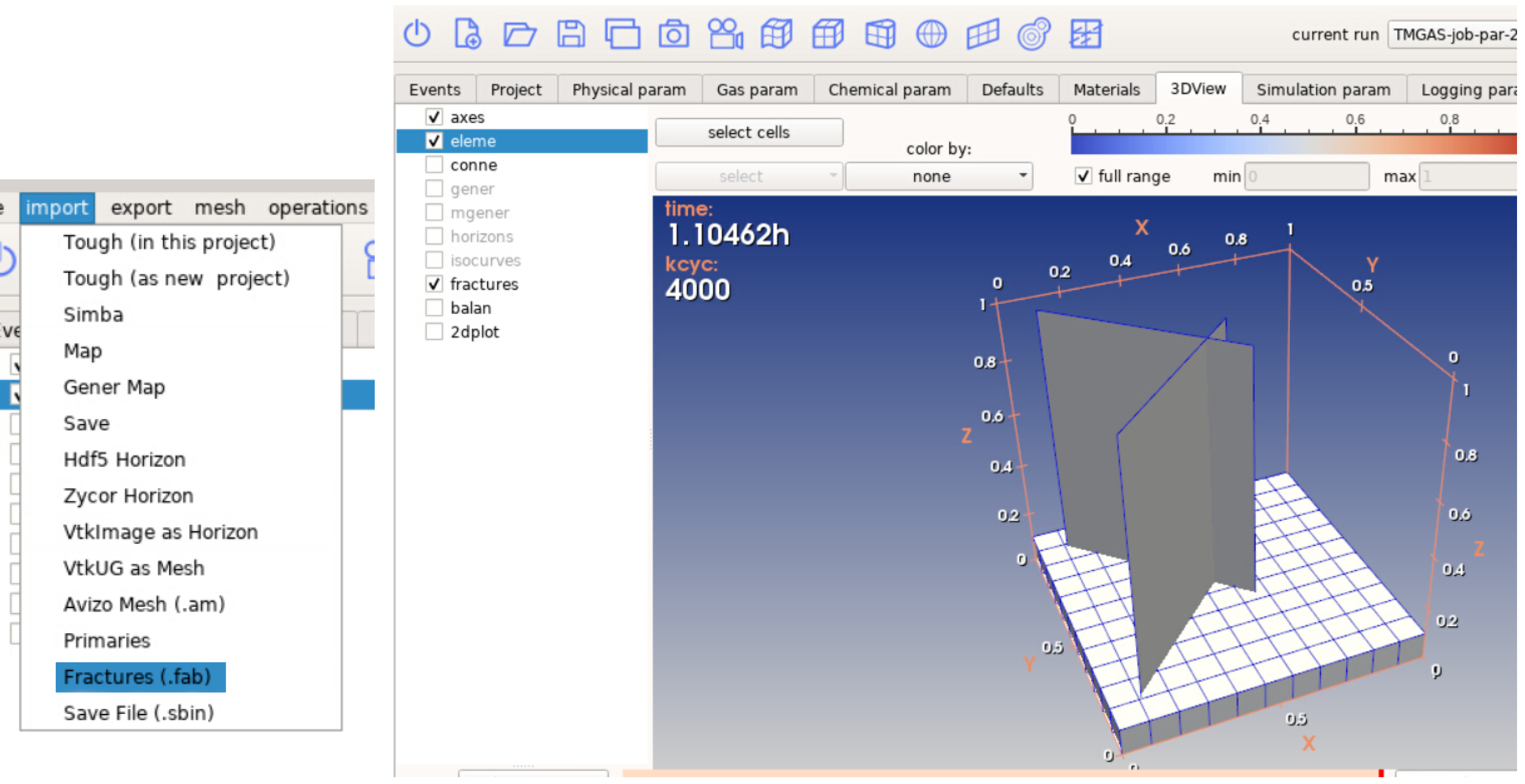
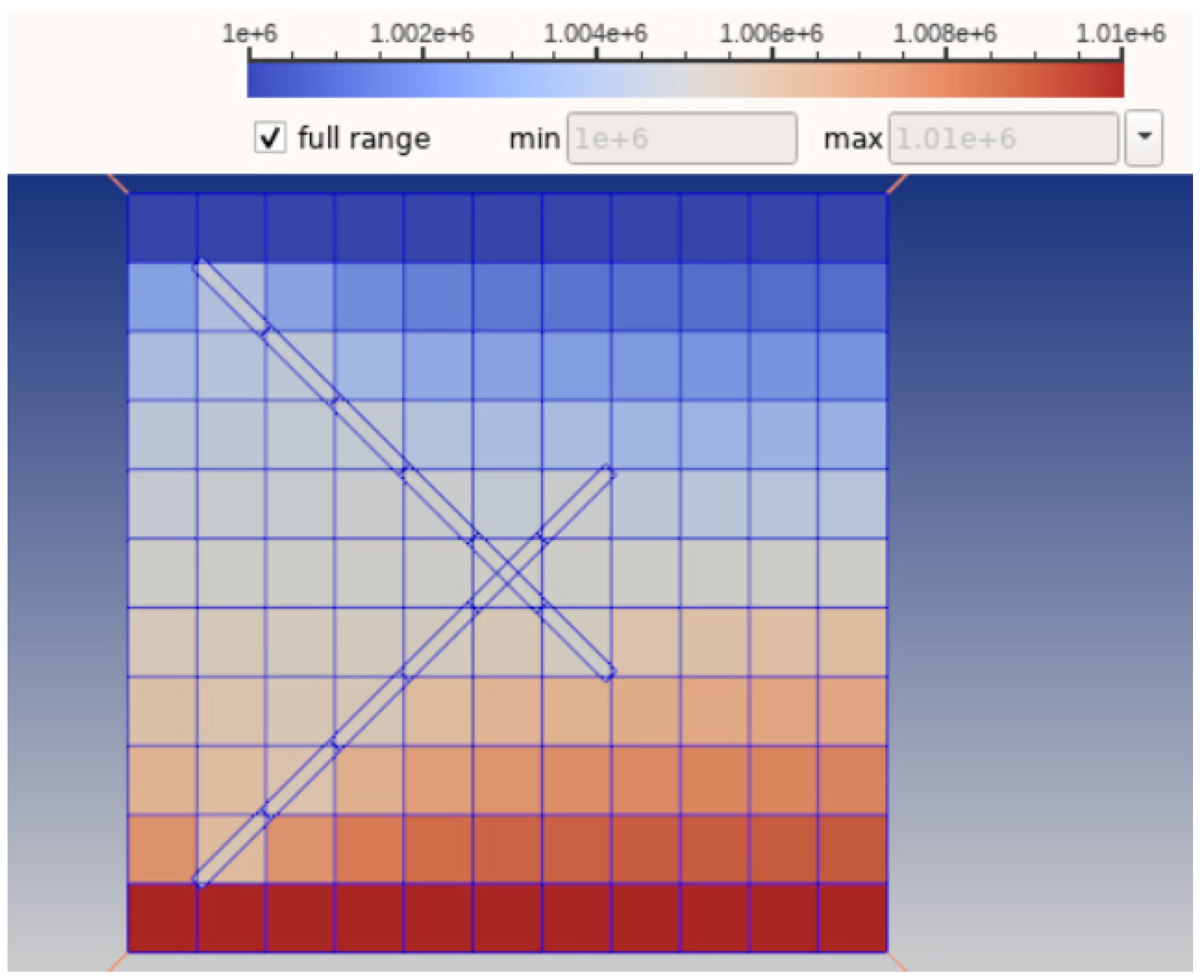
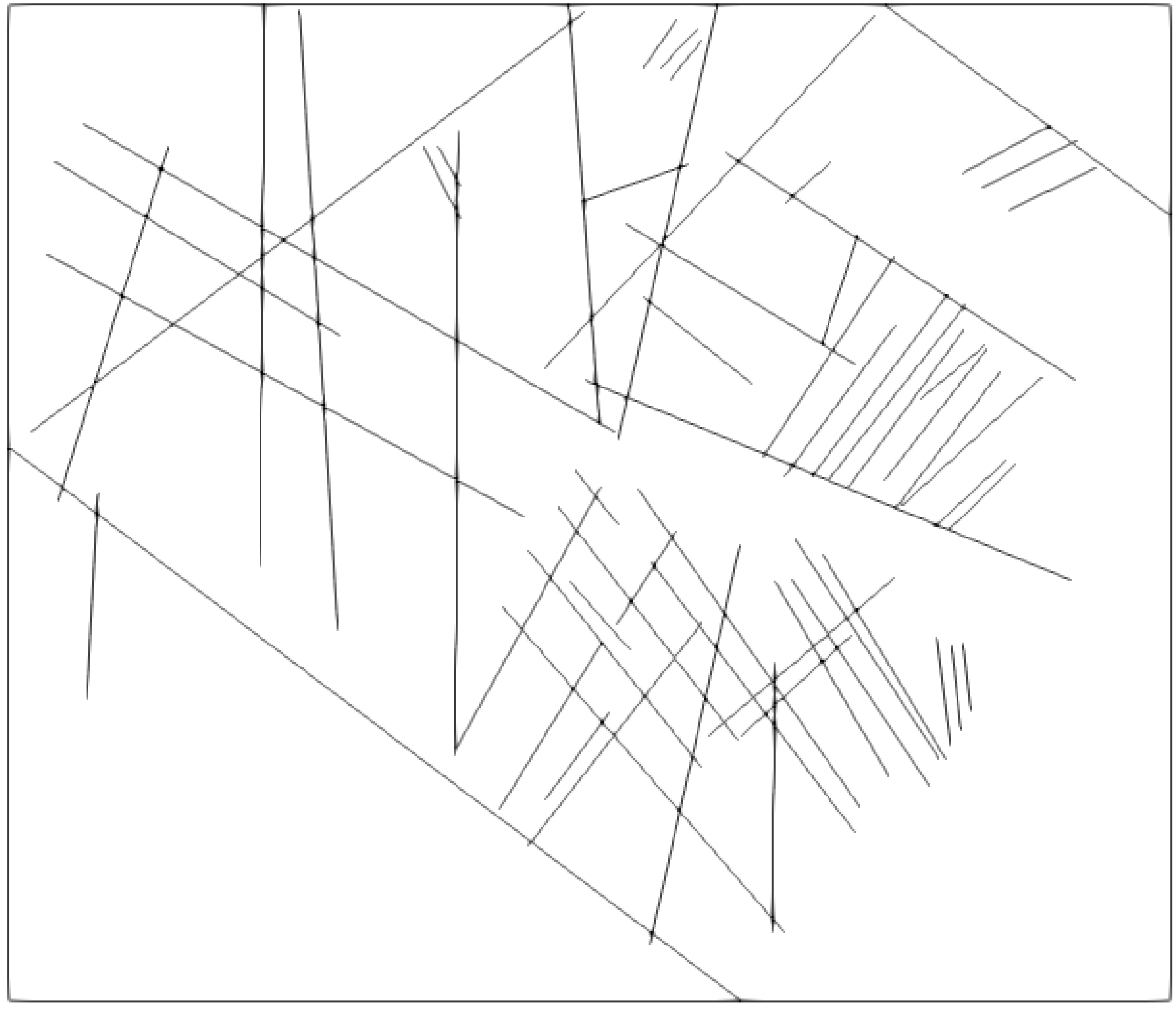
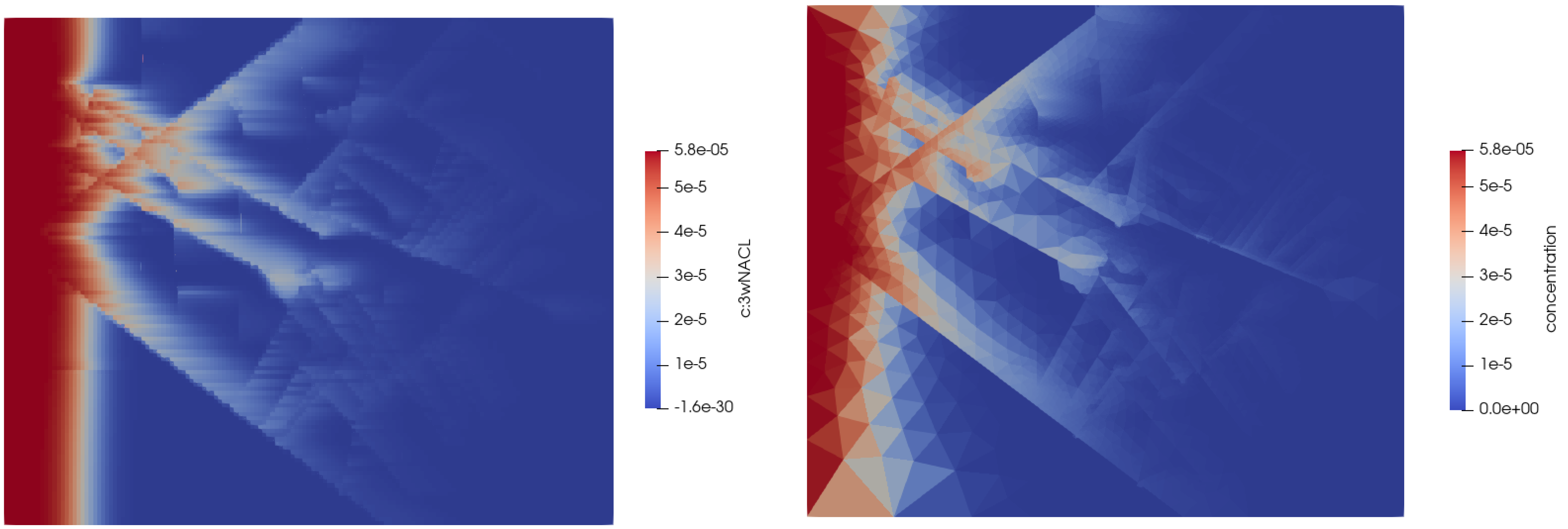
First, a Two Point Flux Discretization (TPFA) Finite Volume (FV) method is written in Matlab and applied to the Darcy equation to simulate porous media flow. Then, a cross-platform C++ code based on make and Cmake is developed using Visual Studio that read VTK matrix grids and evaluate matrix-matrix, matrix-fracture, neighbouring fracture-fracture, and non-neighbouring fracture-fracture transmissibilities needed in the Embedded Discrete Fracture Modeling (EDFM) method. Outputs are transmissibilities and a complex data structure compounding of volumes, surfaces and connections between matrices and fractures. Outputs are exported in an hdf5 file format that can be served as an input in Matlab Reservoir Simulation Toolbox (MRST) to complete the simulation process. Using this technique we can tackle MRST limitations and we would be able to simulate reservoirs with a large number of fractures with arbitrary shapes including non-convex ones. Complex polygon clipping and polygon intersection algorithms are developed in this part to help in the process of evaluating transmissibilities. Moreover, an algorithm is developed to evaluate integrals over these non-convex regions to compute the average normal distance. However, modifications are also needed in the MRST open-source code toolbox, that those also done. After validating code against other available data, then the code has been combined and integrated with unique and extensive industrial software (our partner). Finally, the user could add fractures to their industrial reservoir simulation software with the graphic user interface (GUI) and get the results in real-time.
Results